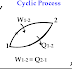
Cyclic process:-
If a system performs the number of processes so that it comes back again to the initial state then the system the number of processes form a closed loop in a thermodynamic diagram which is called a thermodynamic cycle.
Sign convention of work and heat flow:-
The first law of thermodynamics:-
The algebraic sum of net heat and work interaction between a system and its surrounding in a thermodynamic cycle is zero.
∑Q = ∑W
cycle cycle
∮(Q-W)=0
∮𝛅Q-𝛅W=0
►Closed cyclic integral of any point function is a zero.
X is any point function
∮dx=0
∴𝛅Q-𝛅W=dx
Q-W=Δx
This is defined as internal energy.
∴𝛅Q-𝛅W=dE
⇒𝛅Q=𝛅W+dE
∴Q-W=ΔE
⇒Q=W+ΔE
Q1-2-W1-2=E2-E1
Q1-2=W1-2+E2-E1
E=u+K.E+P.E+Any other kind of energy
dE=du+d(K.E)+d(P.E)+d(..........)
Internal energy is a point function.
Limitation of the 1st law of thermodynamics
Internal Energy:-
Internal energy is a property of system whose change in a process executed by the system equals to the difference between heat and work interactions by the system with its surroundings.
. In a thermodynamic process
𝛅Q-𝛅W=dE
where E is the internal energy
. The Internal energy comprises inter-molecular energy kinetic energy potential energy of a system.
✸ For a closed or stationary system, the inter-molecular energy is the only component of internal energy and is usually denoted by the symbol "U".
Q1-2=W1-2+E2-E1
𝛅Q=𝛅W+dE
∮𝛅Q=∮dE+∮𝛅W
E=u+K.E+P.E (for stationary system K.E=0)
dE=du+d(K.E)+d(P.E) (small change in P.E is zero)
dE=du
Q1-2=u2-u1+W1-2
𝛅Q=du+𝛅w
If we consider a closed system which perform only reversible displacement work that means Quasi static displacement work which is nothing but pdv work.
𝛅Q=du+𝛅w
 (for closed system 𝛅w=pdv)
(for closed system 𝛅w=pdv)
𝛅Q=du+pdv
✸ The first law for a closed system in an infinitesimal process can be written as
𝛅Q=du+𝛅w
✸ For a finite process between two states executed by a closed system.
Q1-2=u2-u1+W1-2
✸ For a finite process for per unit mass

✸ For infinite
𝛅Q/𝛅m=du+pdv
If a system performs the number of processes so that it comes back again to the initial state then the system the number of processes form a closed loop in a thermodynamic diagram which is called a thermodynamic cycle.
 |
| cyclic process |
Sign convention of work and heat flow:-
 |
| sign convention for heat and work |
The first law of thermodynamics:-
The First Law of Thermodynamics states that energy can be
converted from one form to another with the interaction of heat, work and
internal energy, but it cannot be created nor destroyed, under any
circumstances. Mathematically, this is represented as
ΔU=q+w
where
ΔU is the total
change in internal energy of a system,
q is the heat
exchanged between a system and its surroundings, and
w is the work done
by or on the system.
∑Q = ∑W
cycle cycle
∮(Q-W)=0
∮𝛅Q-𝛅W=0
►Closed cyclic integral of any point function is a zero.
X is any point function
∮dx=0
∴𝛅Q-𝛅W=dx
Q-W=Δx
This is defined as internal energy.
∴𝛅Q-𝛅W=dE
⇒𝛅Q=𝛅W+dE
∴Q-W=ΔE
⇒Q=W+ΔE
Q1-2-W1-2=E2-E1
Q1-2=W1-2+E2-E1
E=u+K.E+P.E+Any other kind of energy
dE=du+d(K.E)+d(P.E)+d(..........)
Internal energy is a point function.
Limitation of the 1st law of thermodynamics
Internal Energy:-
Internal energy is a property of system whose change in a process executed by the system equals to the difference between heat and work interactions by the system with its surroundings.
. In a thermodynamic process
𝛅Q-𝛅W=dE
where E is the internal energy
. The Internal energy comprises inter-molecular energy kinetic energy potential energy of a system.
✸ For a closed or stationary system, the inter-molecular energy is the only component of internal energy and is usually denoted by the symbol "U".
Q1-2=W1-2+E2-E1
𝛅Q=𝛅W+dE
∮𝛅Q=∮dE+∮𝛅W
E=u+K.E+P.E (for stationary system K.E=0)
dE=du+d(K.E)+d(P.E) (small change in P.E is zero)
dE=du
Q1-2=u2-u1+W1-2
𝛅Q=du+𝛅w
If we consider a closed system which perform only reversible displacement work that means Quasi static displacement work which is nothing but pdv work.
𝛅Q=du+𝛅w
 (for closed system 𝛅w=pdv)
(for closed system 𝛅w=pdv) 𝛅Q=du+pdv
✸ The first law for a closed system in an infinitesimal process can be written as
𝛅Q=du+𝛅w
✸ For a finite process between two states executed by a closed system.
Q1-2=u2-u1+W1-2
✸ For a finite process for per unit mass

✸ For infinite
𝛅Q/𝛅m=du+pdv





Nice sir
ReplyDeleteI am impressed. I don't think Ive met anyone who knows as much about this subject as you do. You are truly well informed and very intelligent. You wrote something that people could understand and made the subject intriguing for everyone. Really, great blog you have got here. Can humans live on mars
ReplyDeleteTHANKS MAN 😊😊
DeleteIf YOU U LIKE our content please share its help me lot