Heat Transfer – Conduction, Convection and Radiation
Thermal Energy Transfer
- Thermal energy can be transferred in
three main ways: conduction, convection, and radiation.
Heat Conduction
- Conduction is the movement of heat within
a solid object.
- Conduction occurs when objects are
touching, such as a kettle on a stove.
- Heat from the flame moves through the
metal of the kettle to the water inside.
- Butter melting on a frying pan is another
example of heat conduction.
Heat Conduction
- Heat conduction occurs through direct
contact when heat moves from a warmer object to a cooler object.
- When you lick an ice cream, it feels cold
because heat conducts from your tongue to the ice cream.
- Heat conduction is the movement of heat
in liquids and gases.
Convection
- Convection is the movement of heat in
liquids and gases.
- In a hot air balloon, the air is heated
by the burner and rises inside the balloon.
- As the hot air rises, the cooler air
falls, creating a current within the balloon.
- The convection current causes thermal
energy in the air to spread. Cooling a Room with an Air Conditioner
- On a hot day, an air conditioner can be
used to cool down a room
- The cold air that blows out from the air
conditioner circulates the room and creates convection currents
Radiation
- Radiation is the process of heat moving from a warmer object to a cooler object without affecting the medium in between.
- Radiation uses electromagnetic waves to emit heat waves that can be reflected, absorbed, or transmitted through a colder object.
- This process doesn't require a medium, unlike conduction and convection.
- For example:- The sun's rays can warm the Earth even after passing through the mesosphere.
Heat Transfer through Conduction and
Convection
- Heat moves from the warmer air to the
colder air, which makes the air in the room cooler
- For the thermal energy to move by
conduction and convection, it must travel through matter
Heat Transfer between the Sun and the
Earth
- The heat transfer between the sun and the
earth occurs through conduction and convection heat Transfer and the Sun's
Warmth
- The sun warms the Earth and other planets
through radiation.
- Radiation is the transfer of energy
through electromagnetic waves.
Radiation vs. Convection
- Radiation is the direct transfer of heat,
as seen when a fireplace warms a person.
- Convection is the transfer of heat
through the movement of a medium, such as the air being warmed in a room by a
fireplace.
- Both radiation and convection play a role
in how the sun's heat reaches and warms the Earth.
Radiant Heat
- Radiant heat is the warmth felt when
placing your hands near an electric heater or other heat source.
- Radiant heat is the direct transfer of
thermal energy through electromagnetic waves, without needing a physical
medium.
- This is the primary mechanism by which
the sun's heat reaches and warms the Earth and other planets in the solar
system. Heat Transfer
- Heat can be transferred in three main
ways: conduction, convection, and radiation.
- Conduction is the transfer of heat
through direct contact between objects or materials, such as heat moving
through the metal of a kettle to the water inside.
- Convection is the transfer of heat
through the movement of a fluid, such as the circulation of hot water within a
kettle.
- Radiation is the transfer of heat through
electromagnetic waves, such as the heat from a heater or campfire.
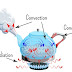
Heat Transfer in a Kettle
- When water in a kettle is heated, thermal
energy moves through the metal of the kettle by conduction.
- The thermal energy then moves around the
water through convection, as the water circulates and mixes.
- Finally, the heat leaves the kettle and
is transferred to the surrounding environment through radiation.
Conclusion
- Heat can be transferred through various
mechanisms, including conduction, convection, and radiation.
- These processes can be observed in
everyday examples, such as water heating in a kettle.







0 comments:
Post a Comment