Thermal reservoir
A thermal energy reservoir (TER) is defined as a large body of infinite heat capacity, which is capable of absorbing or rejecting an unlimited quantity of heat without suffering appreciable changes in its thermodynamic coordinates. The changes that do take place in the large body as heat enters or leaves are so very slow and so very minute that all processes within it are quasi-static.
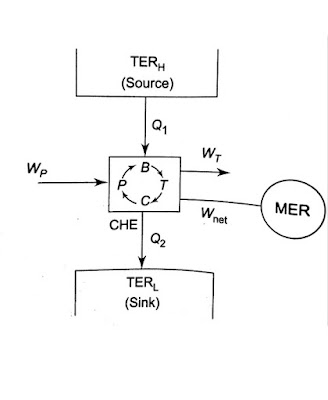
The thermal energy reservoir (TER) from which heat Q1 is transferred to the system operating in a heat engine cycle is called the source. The thermal energy reservoir TER to which heat Q2 is rejected from the system during a cycle is the sink.
A typical source is a constant temperature furnace where fuel is continuously burnt, and a typical sink is a river or sea or the atmosphere itself.
A mechanical energy reservoir (MER) is a large body enclosed by an adiabatic impermeable wall capable of storing work as potential energy (such as a raised weight or wound spring) or kinetic energy (such as a rotating flywheel). All processes of interest within an MER are essentially quasi- static. An MER receives and delivers mechanical energy quasi - statically.
 |
| Thermal reservoir |





0 comments:
Post a Comment