Zeroth Law:-
When two bodies or systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third one then they are in thermal equilibrium with each other.

Properties:-
Intensive properties:-
Thermodynamic equilibrium:-

When two bodies or systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third one then they are in thermal equilibrium with each other.
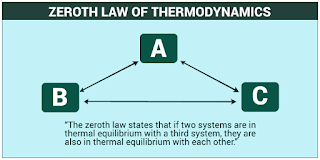 |
| Zeroth law of Thermodynamics |

Properties:-
- Identifiable characteristic features that
describe or specify a system are known as property.
- Properties are the coordinates to describe
the state of a system and therefore they are termed as state variables.
- The important conditions to be fulfilled to
specify the state of a system:-
1.
The
properties must be uniform throughout the system.
2.
The
value of all properties should be invariant with time.
There are two types of property:-
→ Extensive properties
→ Intensive properties
Extensive
properties:-
The
properties which depend on the extent of the system and hence are directly
proportional to the mass of the system are known as extensive properties.
Intensive properties:-
The properties that do not depend
upon the mass of the system and assume finite values even if the mass of the
system approaches zero are known as intensive properties.
Thermodynamic equilibrium:-
A system to be in Thermodynamic
Equilibrium the property should remain variant with time and that should be
uniform within the system.
Thermodynamic equilibrium
#Thermal
equilibrium #Mechanical equilibrium #Chemical equilibrium
Thermal equilibrium:-
The equilibrium states achieved
by two (or more) system, characterized by restricted values of the
thermodynamic property of the system, after they have been in communication with each other through a diathermic wall. For thermal equilibrium temperature
gradient should be zero.
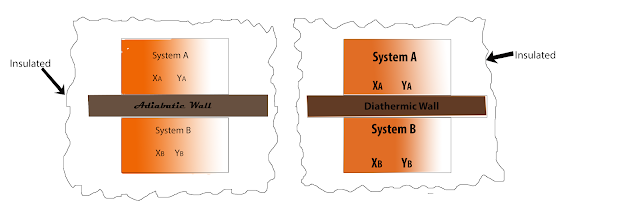 |
| thermal equilibrium |
Mechanical equilibrium:-
In the absence of any unbalance force within the system itself and also between the system and the surroundings, the system is said to be in a state of mechanical equilibrium. If an unbalanced force exits, either the system alone or both the system and the surroundings will undergo a change of state till mechanical equilibrium is attend. For mechanical equilibrium pressure gradient has to be zero.
Chemical equilibrium:-
If there is no chemical reaction or transfer of matter from one part of the system to another, such as diffusion or solution, the system is said to exit in a state of chemical equilibrium.
In the absence of any unbalance force within the system itself and also between the system and the surroundings, the system is said to be in a state of mechanical equilibrium. If an unbalanced force exits, either the system alone or both the system and the surroundings will undergo a change of state till mechanical equilibrium is attend. For mechanical equilibrium pressure gradient has to be zero.
Chemical equilibrium:-
If there is no chemical reaction or transfer of matter from one part of the system to another, such as diffusion or solution, the system is said to exit in a state of chemical equilibrium.
Temperature:-
A thermodynamic property that determines whether or not a system is in thermal equilibrium with other systems.
A thermodynamic property that determines whether or not a system is in thermal equilibrium with other systems.





0 comments:
Post a Comment