Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics:-
Definition 1:- Thermodynamics is the branch of physical science that deals with the relations between heat and other forms of energy (such as mechanical, electrical, or chemical energy), and, by extension, the relationships between all forms of energy.
Definition 2:- Thermodynamics is defined as a fundamental science that describes the basic law in relation to the different physical processes which involved the transfer or transformation of energy and the relation among the different physical properties of substances that are affected by such processes.
Thermodynamics comes from two Greek words Therme and Dynamic.
- There are two views in the study of thermodynamics:-
- Macroscopic or Classical view
- Microscopic or Statistical view
Macroscopic:-
In a microscopic view, attention is made to a certain quantity of matter without consideration of the events occurring at the molecular level.
Microscopic:-
In a microscopic view, the properties of matter are studied at the molecular level.
System:-
A system is defined as a quantity of matter upon which attention is made in the analysis of a problem and this is always bounded by a boundary.
There are generally three types of systems:-
1. Control mass system (closed system )
2. Control volume system (open system)
3. Isolated system
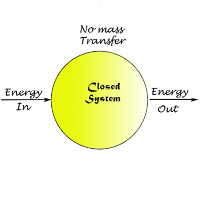
1. Control mass system:-
A system of fixed mass with first identity is known as a control mass system. There is only energy transfer but no mass transfer across the system boundary.
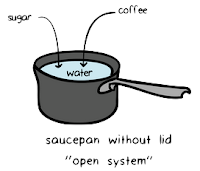
2. Control volume system:-
A system in which matter crosses the system boundary and remains fixed without any change in the volume of the system is known as the control volume system.
3. Isolated system:-
An isolated system is one in which there is neither interaction of mass nor energy between the system and the surroundings.
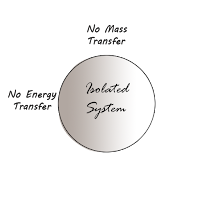 |
| Isolated System |
Adiabatic System:-
An adiabatic system is one that is thermally insulated from its surroundings. It can,
however, exchange work with its surroundings. If it does not, it becomes an isolated system.
Homogeneous System:-
A system that consists of a single phase is termed a homogeneous system. Examples :
A mixture of air and water vapor, water plus nitric acid, and octane plus heptane.
Heterogeneous System:-
A system that consists of two or more phases is called a heterogeneous system. Examples :
Water plus steam, ice plus water, and water plus oil.
An adiabatic system is one that is thermally insulated from its surroundings. It can,
however, exchange work with its surroundings. If it does not, it becomes an isolated system.
Homogeneous System:-
A system that consists of a single phase is termed a homogeneous system. Examples :
A mixture of air and water vapor, water plus nitric acid, and octane plus heptane.
Heterogeneous System:-
A system that consists of two or more phases is called a heterogeneous system. Examples :
Water plus steam, ice plus water, and water plus oil.
Boundary:-
The boundary is a solid boundary or may not be a solid boundary and sometimes boundary may be an imaginary boundary. Which separates the system and its surrounding area known as the boundary of the system.









0 comments:
Post a Comment